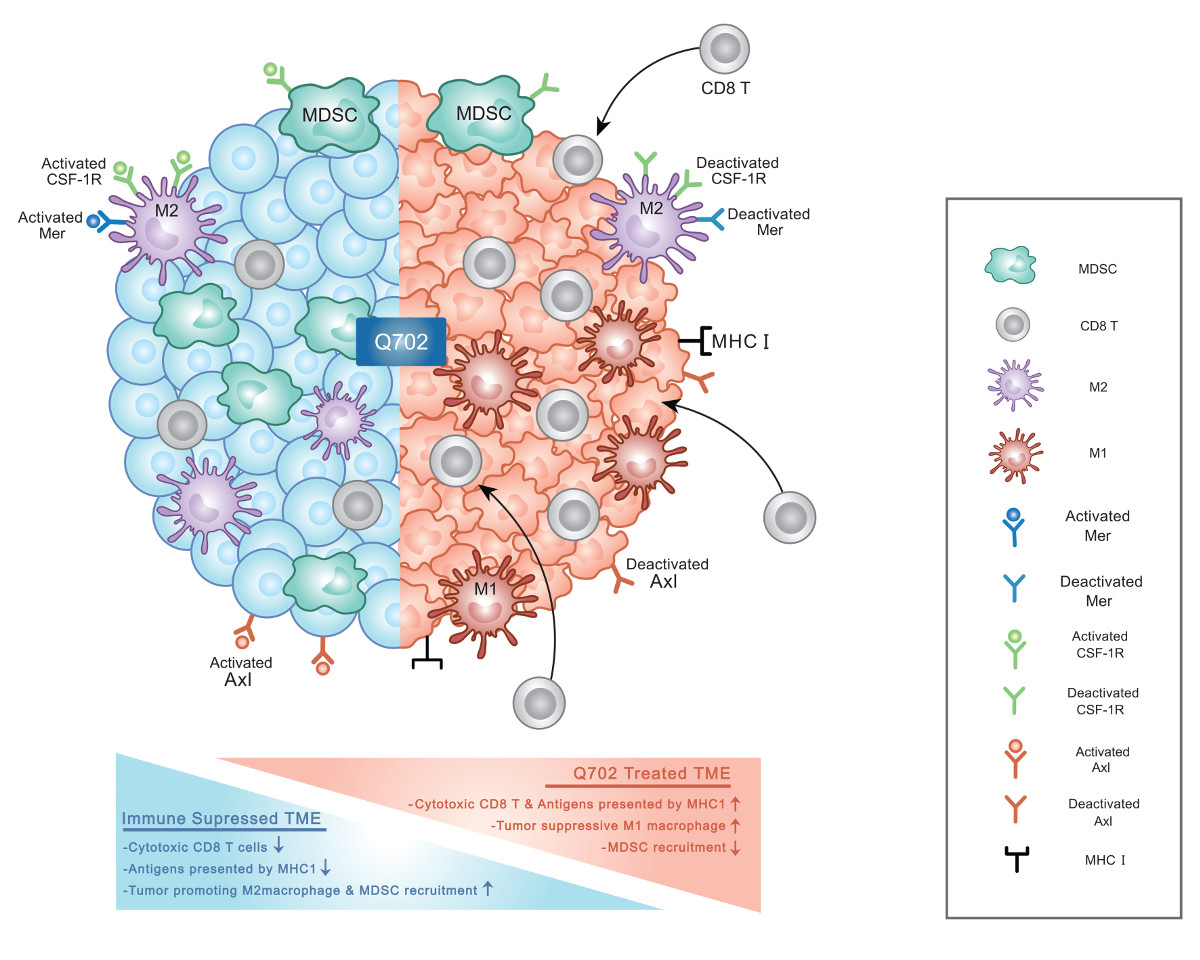
Q702: A Novel Axl/Mer/CSF1R Triple Kinase Inhibitor
Q702 is an orally available, selective inhibitor of Axl, Mer, and CSF1R receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), demonstrating potent anti-tumor activity through immune activation and chemo-sensitization in various tumor models.
By targeting key pathways involved in immune suppression, drug resistance, and tumor progression, Q702 has the potential to improve treatment outcomes across multiple cancer types and hematologic malignancies.
Targeting Tumor Immune Evasion & Drug Resistance
Axl and Mer RTKs play critical roles in cancer progression by promoting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), enhancing drug resistance, and suppressing innate immune responses.
Their activity makes tumors more resilient to therapies, particularly in the context of T cell checkpoint inhibitors.
CSF1R further contributes to tumor immune evasion by regulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) through tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), both of which suppress anti-tumor immunity.
By selectively inhibiting Axl, Mer, and CSF1R, Q702 restores innate immune function and sensitizes tumors to both immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Preclinical studies demonstrate that Q702 is effective as a monotherapy and in combination with checkpoint inhibitors, particularly in immune-suppressed conditions where innate immunity is critical.
Q702 in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease (cGvHD)
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is a life-saving treatment for blood cancers but carries the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD).
Chronic GvHD (cGvHD) is associated with fibrosis driven by M2 macrophages, which are regulated by CSF1R.
By inhibiting CSF1R, Axl, and Mer, Q702 reduces M2 macrophage differentiation and fibrosis, as demonstrated in preclinical models.
In an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) model, Q702 improved survival, reduced fibrosis scores, and lowered collagen levels. Similarly, in a liver fibrosis model, Q702 significantly reduced fibrotic tissue.
These findings suggest Q702 has the potential to alleviate cGvHD by targeting CSF1R-dependent macrophages and fibrosis.
Q702 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Relapsed or refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains a major clinical challenge, with poor survival rates and limited response to standard treatments.
While venetoclax-based regimens have improved some outcomes, resistance remains a significant issue.
Overexpression of Axl, Mer, and CSF1R is associated with poor prognosis in AML. Targeting Axl and Mer has shown efficacy as monotherapy and in combination with venetoclax, particularly in aggressive subtypes such as FLT3-ITD AML and venetoclax-resistant AML. CSF1R inhibition further disrupts survival signals in the leukemia microenvironment, weakening the tumor’s ability to evade therapy.
Q702 enhances anti-leukemic immunity by targeting Axl/Mer in macrophages while simultaneously blocking CSF1R-mediated tumor support. Preclinical studies suggest that combining Q702 with venetoclax and azacitidine may improve treatment outcomes for AML patients. This potential has led to a clinical trial collaboration with MD Anderson to explore Q702 in AML.
Q702 in Other Hematologic Malignancies
The TAM kinase family (TYRO3, Axl, and Mer) plays a key role in tumor survival and immune evasion across various hematologic malignancies.
Axl overexpression is linked to chemotherapy resistance in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL) and multiple myeloma by activating survival pathways such as AKT, ERK, and NF-kB. Mer expression further promotes immune suppression by driving M2 macrophage polarization.
CSF1R regulates the immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment by driving TAM differentiation and MDSC recruitment. Its role in AML, Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH), and Erdheim-Chester Disease (ECD) has made it a promising therapeutic target. Clinical evidence supports CSF1R inhibition in these conditions, including reports of complete responses in refractory ECD cases.
By selectively targeting Axl, Mer, and CSF1R, Q702 disrupts tumor survival mechanisms, reduces M2 macrophage activity, and enhances anti-tumor immunity. Preclinical data show that Q702 induces dose-dependent cytotoxicity, triggers apoptosis, and significantly inhibits tumor growth. These promising findings have led to a clinical trial collaboration with Mayo Clinic to explore Q702 in histiocytosis and other hematologic malignancies.
Poster
1. Q701, a selective Axl/Mer inhibitor as an immune checkpoint inhibitor (2017 AACR-NCI-EORTC poster)
2. Q702, Selective Axl, Mer and CSF1R triple kinase inhibitor with dual potentials leading to tumor regression (2019 AACR annual meeting)
3. Q702, selective Axl/Mer/CSF1R triple kinase inhibitor enhance the activity of immune checkpoint inhibitor by alteration of immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (2020 AACR poster)
4. Patient pharmacodynamic biomarker and PK evaluation results from an ongoing phase I dose-escalation study of Q702,
an Axl, Mer and CSF1R kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumors (2023 AACR poster)
5. A Phase 1, Multicenter, Open-label, Dose-Escalation, Safety, Pharmacokinetic Study of Q702 with a Cohort Expansion at the RP2D in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors (2023 SITC poster)
6. A Phase 1B/2, Open-label Study of Q702 in combination with intravenous Pembrolizumab in Patients with Selected Advanced Solid Tumors (2023 SITC poster)
7. First in Human Trial of Q702 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. (2025 AACR poster)
8. A Phase 1b/2, Open-Label Study of Selective Axl, Mer and CSF1R Inhibitor Adrixetinib (Q702) in Combination with Intravenous Pembrolizumab in Patients with Selected Advanced Solid Tumors: Results of a Phase 1 Study (QRNT-008) (2025 ASCO poster)
Publications
1. A Novel Selective Axl/Mer/CSF1R Kinase Inhibitor as a Cancer Immunotherapeutic Agent Targeting Both Immune and Tumor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment (MDPI)
Clinical Trials
1. Oral Axl/Mer/CSF1R Selective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumor (NCT04648254)
2. Oral Axl/Mer/CSF1R Selective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Q702 in Combination With Pembrolizumab in Patients With Selected Advanced Solid Tumors (NCT05438420)
3. Phase I Study of Q702 with Azacitidine and Venetoclax for Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia (NCT06445907)
4. Q702 for the Treatment of Patients With Hematologic Malignancies (NCT06712810)
Related News & publications
1. The E3 ligase Cbl-b and TAM receptors regulate cancer metastasis via natural killer cells. Nature, 507(7493),508-12, 2014; (Mar, 27) (Pubmed)
2. Killer targets in metastasis (SciBX)
3. Qurient Announces U.S. FDA Clearance of IND Application for Q702, a Novel Cancer Immunotherapy (businesswire)
4. Qurient Enrolls First Patient in Q702 U.S. Phase 1 Study (businesswire)
5. Qurient Announces Collaboration Agreement with MSD to Evaluate Selective Triple Inhibitor Q702 in Combination With KEYTRUDA® (pembrolizumab) (businesswire)
6. Qurient Announces Dosing of First Patient in Q702 in Combination with KEYTRUDA® in a Phase 1b/2 Clinical Study for the Treatment of Patients with Solid Tumors (businesswire)
7. Qurient Launches Clinical Trial for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment with Adrixetinib (Q702) (businesswire)
 Q702 : Axl/Mer/CSF1R Triple Inhibitor
Q702 : Axl/Mer/CSF1R Triple Inhibitor