Q901: A Next-Generation CDK7 Inhibitor.
Q901 is a highly selective and potent CDK7 inhibitor designed to target multiple hallmarks of cancer, including uncontrolled cell cycle progression, DNA damage repair, and resistance to ADC therapies. By disrupting key regulatory pathways, Q901 has demonstrated strong potential in overcoming drug resistance and enhancing the efficacy of combination treatments.
Halting Cancer Cell Division & Overcoming CDK4/6 Resistance
Cancer cells proliferate uncontrollably due to dysregulated cell cycle progression.
While CDK4/6 inhibitors have been effective in hormone receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancer, resistance often develops through mutations in the RB protein or alternative signaling pathways.
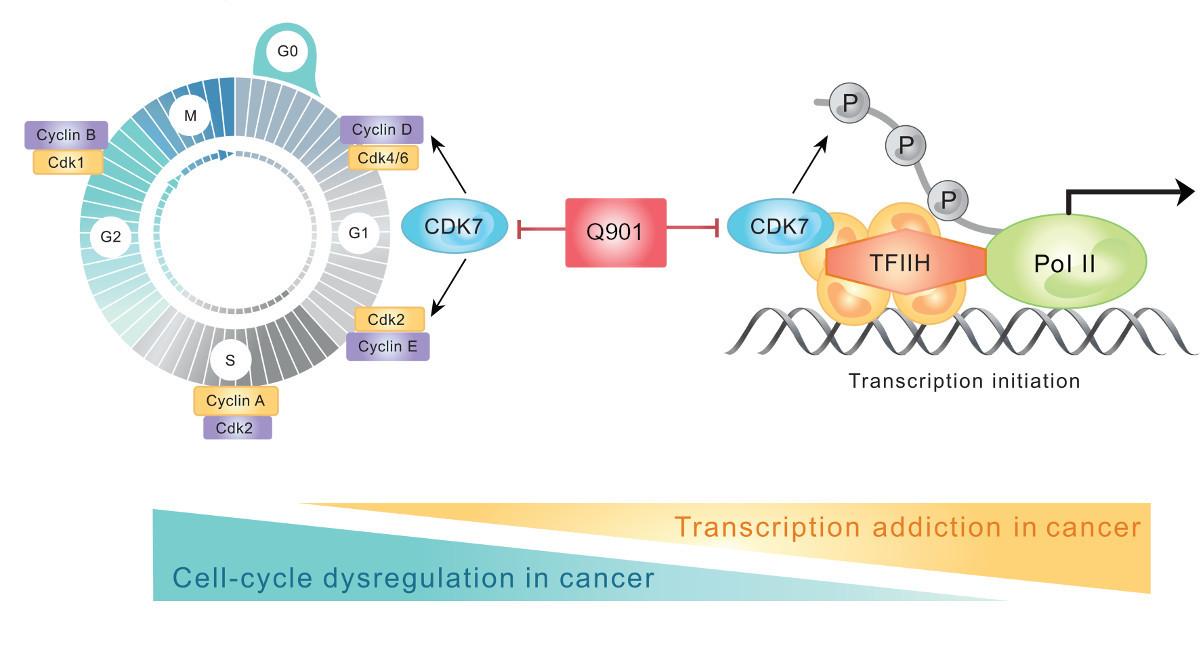
Q901 inhibits CDK7, a master regulator that activates multiple cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK4, CDK6, CDK1, and CDK2), effectively halting cancer cell division.
By targeting CDK7, Q901 not only overcomes resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors but also remains effective in cancers where the RB pathway is altered or bypassed.
Disrupting DNA Damage Repair (DDR) Pathways
Beyond its role in cell cycle regulation, CDK7 is essential for RNA transcription.
As a key subunit of the general transcription factor TFIIH, CDK7 regulates RNA transcription by phosphorylating RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) and modulating CDK9 activity.
Rapidly dividing cancer cells accumulate significant DNA damage and rely on enhanced DNA Damage Response (DDR) pathways for survival.
Q901 disrupts DDR by blocking the transcription of critical DNA repair genes (e.g., BRCA, RAD51, LIG1), leading to irreparable DNA damage and cancer cell death.
Unlike traditional DDR inhibitors that target a single repair protein, Q901 broadly suppresses multiple DDR genes, making it a powerful strategy against DNA repair-dependent cancers.
Enhancing Immunotherapy via Genomic Instability
Cancers with high microsatellite instability (MSI-H) or defective mismatch repair (MMR-d) respond well to immune checkpoint inhibitors like Keytruda (pembrolizumab).
Q901 induces genomic instability by inhibiting DDR pathways, converting resistant tumors into immunotherapy-sensitive ones.
This potential has led to a clinical trial collaboration with Merck to explore Q901 in combination with Keytruda.
Synergy with Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) deliver cytotoxic agents specifically to cancer cells. Many ADCs induce lethal DNA damage, but resistance can develop due to heightened DDR activity. Q901 enhances ADC efficacy by suppressing DDR transcription, preventing cancer cells from repairing ADC-induced damage and making tumors more susceptible to treatment.
Q901 is particularly synergistic with topoisomerase 1 inhibitors (TOP1i) based ADCs as CDK7 inhibitor induces ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of RNA polymerase II and prevents the proteasomal degradation of TOP1-DPCs (DNA-protein cross-links). These actions enhances ADC-induced cancer cell death, rendering cancer cells hypersensitive to TOP1i-based ADCs (doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0891). This potential has led to a clinical trial collaboration with NCI to explore Q901 in combination with TOP1i ADC.
Currently in Phase 1/2 clinical trials, Q901 is being evaluated for its safety and efficacy in advanced solid tumors, offering a promising new option for patients with treatment-resistant cancers.
Poster
1. Highly selective, orally available CDK7 inhibitor for cancer therapy (2017 AACR-NCI-EORTC poster)
2. Development of highly selective CDK7 inhibitor Q901 for solid tumors (2020 AACR poster)
3. Q901, Selective CDK7 inhibitor, the new strategy for overcoming primary and acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER-positive breast cancer(2021 AACR poster)
4. Q901, a highly selective covalent CDK7 inhibitor inducing substantial anti-tumor effect in a broad spectrum of solid tumor lineages. (2022 AACR poster)
5. Evaluation of the potential combination regimens for Q901,a clinical stage selective CDK7 inhibitor, as a DNA damage repair inhibitor. (2023 AACR poster)
6. A Phase 1/2 Multicenter, Open-label, Dose-escalation, Safety, Pharmacodynamic, and Pharmacokinetic Study of Q901 Administered via Intravenous Infusion in Adult Patients with Selected Advanced Solid Tumors with a Cohort Expansion at the Recommended Phase 2 Dose. (2023 ESMO poster)
7. Functional Dissection of CDK7 in Transcription Using a highly Selective CDK7 Inhibitor Q901. (AACR 2024)
8. A first-in-human trial of selective CDK7 inhibitor Q901, in patients with advanced solid tumors: Interim results of a phase I study (QRNT-009) (2024 ASCO)
Clinical Trials
1. Highly Selective CDK7 Inhibitor Q901 in Selected Advanced Solid Tumors (NCT05394103)
Related News
1. Qurient Announces U.S. FDA Clearance of IND Application for Q901, a Novel Cancer Therapy (FDA)
2. Qurient Announces Collaboration Agreement with MSD to Evaluate Selective CDK7 Inhibitor Q901 in Combination With KEYTRUDA® (pembrolizumab) (businesswire)
3. Qurient Announces Dosing of First Patient in Q901 Phase 1/2 Clinical Study for the Treatment of Patients with Solid Tumors (businesswire)
4. Qurient Therapeutics Enters CRADA with the National Cancer Institute to Collaborate on a Phase 1/2 Clinical Study of Q901 in Combination with TROP2-ADC (BioSpace)
 Q901 : highly selective CDK7 inhibitor
Q901 : highly selective CDK7 inhibitor